MRI of the Liver
Study Description
MRI of the liver is routinely performed with gadolinium contrast to detect and characterize liver masses and to assess hepatic perfusion. Standard gadolinium agents provide information on lesion vascularity during the dynamic or extracellular post-gadolinium phase, but do not assess hepatocyte function.
Eovist® (gadoxetate disodium) is a gadolinium-based contrast agent that is actively taken up by hepatocytes and excreted into the bile. It therefore provides additional functional information that can help detect and further characterize liver lesions during the hepatocyte phase. For example, a focal liver metastasis will appear as an area of low T1 signal on a background of high T1 signal caused by Eovist excretion from normal parenchyma. Certain benign lesions may be definitively identified using Eovist, helping avoid an unnecessary liver biopsy.
Since Eovist is excreted into the bile ducts, it may also be used to generate T1-weighted maps of the biliary system. This may serve as a useful complement to T2 based MR cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) which can be degraded by adjacent inflammation and magnetic susceptibility artifact from surgical clips.
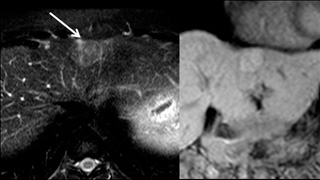
Patient Selection and Indications
Liver imaging procedures may be performed for various reasons including laboratory abnormalities, jaundice, and abdominal pain. Liver lesions are often found incidentally during imaging studies performed for another indication, and such findings often require further assessment.
While CT and ultrasound may be used to evaluate the liver, MRI is more sensitive and specific for non-calcified liver lesions. It is the modality of choice for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) screening in patients with risk factors such as hepatitis or cirrhosis. It is also used to screen potential donors for liver transplant.
In general, a conventional liver MRI is performed first, as this exam is technically easier to perform and contrast kinetics are more predictable. However, certain lesions are better assessed using an Eovist MRI of the liver. If a lesion is best characterized by Eovist, the radiologist will recommend a follow up exam using that agent.
Indications
- Radiologist recommendation
- Enhancing liver lesion which “fades” to isointensity.
- Suspected focal nodular hyperplasia.
- HCC surveillance, particularly follow-up of baseline exam.
- To exclude subtle liver metastasis in a potential surgical or transplant candidate.
- Reproducible tumor measurements in tumors with variable enhancement kinetics such as carcinoid metastases.
- T1 MRCP, especially if a stricture or bile leak is suspect and T2 MRCP is inconclusive. This in an off-label indication.
- Lesion targeting during MRI guided liver biopsy
Contraindications
- No prior conventional MRI and no radiologist recommendation
- Enhancing liver lesion which “washes out” to hypointensity. These often require biopsy.
- Suspected hemangioma on CT or ultrasound
- Cholangiocarcinoma
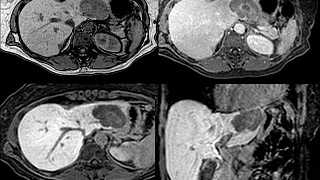
Patient Preparation
Standard MRI Precautions should be employed. Please specify if T1 MRCP imaging is desired.
Eovist® is administered at 0.025 mmol/kg body. It is contraindicated in renal failure due to the risk of NSF although it is theoretically safer than other gadolinium agents due to its combined renal and hepatic routes of excretion.
The entire examination takes approximately 30 minutes although if a T1 MRCP is performed it may take longer. The hepatocyte phase lasts up to several hours, so after dynamic post gadolinium images are obtained, the patient may elect to take a break before continuing with the exam.
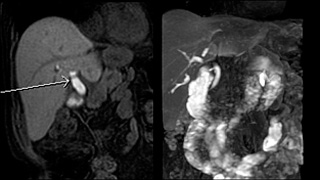
Reporting and Outcomes
Liver MRI provides excellent image quality. Soft-tissue contrast is superior to competing modalities. It provides an extremely sensitive depiction of fluid and edema. The addition of Gadolinium increases detection of subtle lesions and allows assessment of multiple vascular phases. Use of Eovist provides additional functional information and can be used to determine if a lesion contains hepatocytes. This information can often help the patient avoid a liver biopsy. It is the examination of choice for identifying focal nodular hyperplasia. It can also help target liver lesions if an MR guided biopsy is indicated.
Every Eovist MRI exam is reviewed by a board-certified radiologist with subspecialty training in advanced body imaging. A comprehensive report detailing findings in the abdomen and in the liver is provided to the referring clinician. As the abdomen is imaged during an Eovist liver MRI, pathology in other organs may be detected incidentally. If urgent findings are encountered, these are relayed in real time by telephone. A copy of the examination and report is furnished to the patient upon request. The exam may also be reviewed directly with the radiologist in the radiology department at a Wellstar facility.