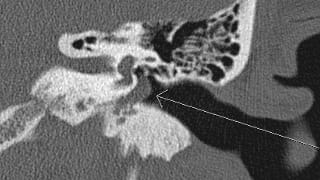
CT of the Temporal Bones Without Contrast
Study Description
High-resolution non-contrast CT of the petrous temporal bones, with special attention to the external auditory canals (EACs), tympanic cavities, ossicles, mastoids, bony labyrinth, and bony internal auditory canal (IACs).
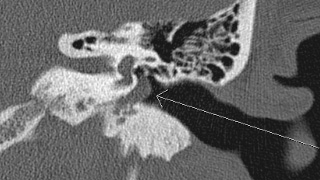
Patient Selection and Indications
- Conductive hearing loss
- Retrotympanic mass
- Acquired or congenital cholesteatoma
- Tinnitus (but CT angiogram may be performed for pulsatile tinnitus as well)
- Otalgia
- Otorrhea
- Ossicular prosthesis evaluation
- Cochlear implant planning and evaluation
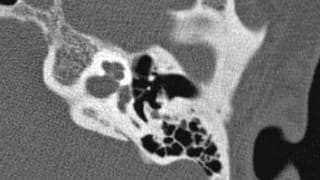
Patient Preparation
The exam should be performed at a center with a 16 (or greater) slice CT scanner. No intravenous contrast is required.
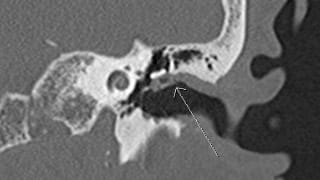
Reporting and Outcomes
Thorough evaluation temporal bones, including the external auditory canals, tympanic cavities, ossicles, mastoids, bony labyrinths, facial nerve canals, bony internal auditory canal, vestibular aqueducts, petrous apices, carotid canals, and jugular bulbs.
Evaluate for potential:
- Benign or malignant masses and mass-like lesions (EAC squamous cell carcinoma, osteoma, or exostoses; keratosis obturans; cholesteatoma; cholesterol granuloma; middle ear adenoma, schwannoma, meningioma, or rhabdomyosarcoma; glomus tympanicum paraganglioma; endolymphatic sac tumor; facial nerve hemangioma).
- Vascular lesions (aberrant or lateralized internal carotid artery, persistent stapedial artery, high-riding or dehiscent jugular bulb, jugular bulb diverticulum).
- Infectious and inflammatory conditions (necrotizing otitis externa, otitis media, mastoiditis, otomastoiditis, apical petrositis, labyrnthitis, otosyphilis, medial canal fibrosis, labyrinthine ossificans, ossicular erosions, tympanosclerosis, fenestral and cochlear otosclerosis).
- Congenital lesions (congenital cholesteatoma, EAC atresia, oval window atresia, labyrinthine or cochlear aplasia, common cavity anomaly, cystic cochleovestibular anomaly, semicircular canal dysplasia, large endolymphatic sac anomaly, aberrant or lateralized internal carotid artery, persistent stapedial artery, high-riding jugular bulb, congenital cephalocele/meningoencephalocele).