3D Imaging Services
Study Description
It’s no surprise that Computed Tomography has made such remarkable strides in technological advancement in recent years; sub-millimeter slices and sub second acquisitions have enabled highly resolute, isotropic scan data. With advanced hardware and software, we can reconstruct that data into multiple planar views without the loss of resolution. This effectively changes the way we look at things entirely. Advanced 3D post-processing has taken this modality and propelled its use and effectiveness well beyond the axial perspective by creating multiple rendering methods that assist in the diagnostic outcome of the patients we serve.
Q3D is a subsidiary of Quantum Radiology and was formed in partnership with Wellstar Health System to provide the cutting-edge 3D services. Our beginnings came from the design of Dr. Jay Cinnamon, a Quantum neuroradiologist. His unique vision, coupled with relationships among advanced medical 3D innovators and colleagues, led to our creation in mid-2004. The goal of the Q3D service is to promote higher levels of depth, quality and insight in the examinations we perform. Q3D is committed to improving patient care and enhancing physician perspective by providing state of the art, comprehensive 3D imaging services that assist in diagnosis and improve clinical outcome.
As medical imaging examinations change and grow, we are poised to accept any new challenges presented to us. If any clinician would like to see new medical imaging initiatives presented through the 3D lab, please do not hesitate to contact us. We will assist you in protocol development and design as well as interfacing with medical imaging management to provide seamless implementation.
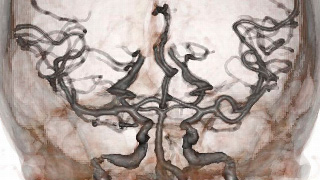
Patient Selection and Indications
All CT Angiography exams automatically generate a request for 3D Imaging workup. Other indications that automatically generate a request for 3D include: CT Urography, CT Pancreatic protocol, CT Liver Volume protocol.
All CT Angiography examinations require the use of Iodinated contrast material. Please see the section on Iodinated Contrast precautions for contraindications.
It is necessary to request 3D Imaging on your imaging order form for the following examinations:
- 3D volumetric analysis
- Dental / Facial CT
- Musculoskeletal CT
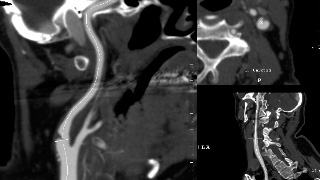
Patient Preparation
A Calcium Scoring is a non-invasive test to detect calcified plaque in the coronary arteries. It is quantified and compared with research statistics to determine an individual’s risk based on similar age and gender patient population.
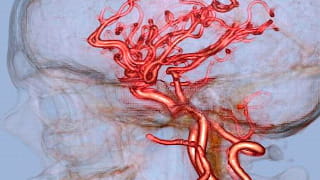
Reporting and Outcomes
A Calcium Scoring is a non-invasive test to detect calcified plaque in the coronary arteries. It is quantified and compared with research statistics to determine an individual’s risk based on similar age and gender patient population.
Greater amounts of calcium deposits in a person’s arteries, as measured by a CT scan, increase the likelihood of a future coronary event such as a heart attack, angina, or death from coronary heart disease, according to a study funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health. This study is the first to confirm this finding in multiple ethnic groups. The findings, titled “Coronary Calcium as a Predictor of Coronary Events in Four Ethnic Groups,” from NHLBI’s Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) are published in the March 27, 2008, issue of the New England Journal of Medicine.
A coronary calcium scan is most useful for patients at moderate risk for a heart attack. People who are at moderate risk have a 10–20% chance of having a heart attack within the next 10 years. This can be estimated using the Risk Assessment Tool from the National Cholesterol Education Program.
Low risk individuals who have a family history of coronary artery disease may also benefit from a coronary calcium scan.
Individuals at high risk or who already have known atherosclerotic disease are unlikely to benefit from this exam. Other imaging options such as a coronary CT angiogram or a cardiac MRI may be more appropriate in such patients.
A sample report is provided at right. The specific calcified vessels are identified along with a total coronary calcium score. A graph showing the patient’s score relative to their cohort is provided, as is a table indicating relative risk. Higher risk may justify more aggressive medical intervention, additional non-invasive testing, and even coronary intervention.
In addition to assessing the coronary calcium score, the cardiac radiologist performs a comprehensive evaluation of all imaged thoracic anatomy. This includes the mediastinum, upper abdomen, lung parenchyma, and osseous structures. The radiologists report may provide additional recommendations based on unexpected but clinically relevant findings.
All results are immediately available to Wellstar affiliated physician via the Wellstar Portal. Otherwise, results may be mailed to the patient and/or outside referring MD.
The exam should only be performed at a center with a 64-slice CT scan or better to minimize cardiac motion artifacts. The patient may need a low-dose ß-blocker to lower HR to < 65. Higher heart rates may be permitted with the faster 256-slice CT scanner at Wellstar Kennestone Hospital. The test is not suitable for patients with irregular heart beat or those who are pregnant.
A summary image dataset labeled “Q3D” is saved as an additional series on PACS. This dataset contains various MIP (maximum intensity projection), VR (volume rendered), Multiplanar, and CMPR (curved multiplanar reformatted images) all depicting a reproducible, methodological approach to the exam specific vascular anatomy.
The 3D dataset is then reviewed with the original CT data by sub-specialized radiologists in cardiac, body, interventional, or neuroradiology and a dictated report is generated as well as direct communication with the referring doctor if needed.

